- Enseignant: Aicha Chadli
- Enseignant: Admin User
- Enseignant: Admin User
- Enseignant: Admin User
- Enseignant: Admin User
- Enseignant: Admin User
- Enseignant: mohamed gorine
- Enseignant: Admin User
The quest for knowledge is at the heart of science. We all have the right to our own opinions as human beings, but we
do not have the right to our own facts. A fact is reality as we understand it, and truth is discovered via scientific
procedures. Based on their observations and current understanding of the subject, scientists will formulate a null
hypothesis about how it functions. They will then conduct an experiment, evaluate the results, and reject the null
hypothesis.
Being skeptical, the scientist either rejects the null hypothesis outright or fails to do so in light of the data analysis.
Eventually, scientists write up the results of the experiment in the form of a research paper and submit it in a journal
related to the specialtyin question. (cf. p.11) * (cf. p.11)
Nair, P. R., & Nair, V. D. (2014
- Enseignant: Admin User
Cette matière permet aux étudiants d’appréhender la complexité de la notion de toxicité et les outils d’évaluation de l’impact des substances toxiques sur les organismes vivants et de leur comportement dans le milieu physique.
Contenu de la matière
PARTI I : NOTIONS DE BASE DE L’ECOTOXICOLOGIE
1) Histoire de l’écotoxicologie
2) Pollution et polluants
3) Dispersion des polluants dans le biotope
4) Transfert des polluants dans la biocénose
5) Toxicodynamie et paramètres de toxicité
6) Toxicocinétique
PARTIE II : OUTILS DE L’ECOTOXICOLOGIE
1) Bioindicateurs
2) Utilisation de bioindicateurs en écotoxicoogie rétrospective
2-1- Utilisation supraindividuelle
2-2- Utilisation infraindividuelle
3) Utilisation de bioindicateurs en écotoxicoogie prédictive
3-1- Bioessais
3-2- Mésocosme
4) Évaluation locale des risques pour les organismes du sol (calcule du PNEC et du PEC)- Enseignant: benkhedda belhaouari
- Enseignant: Admin User
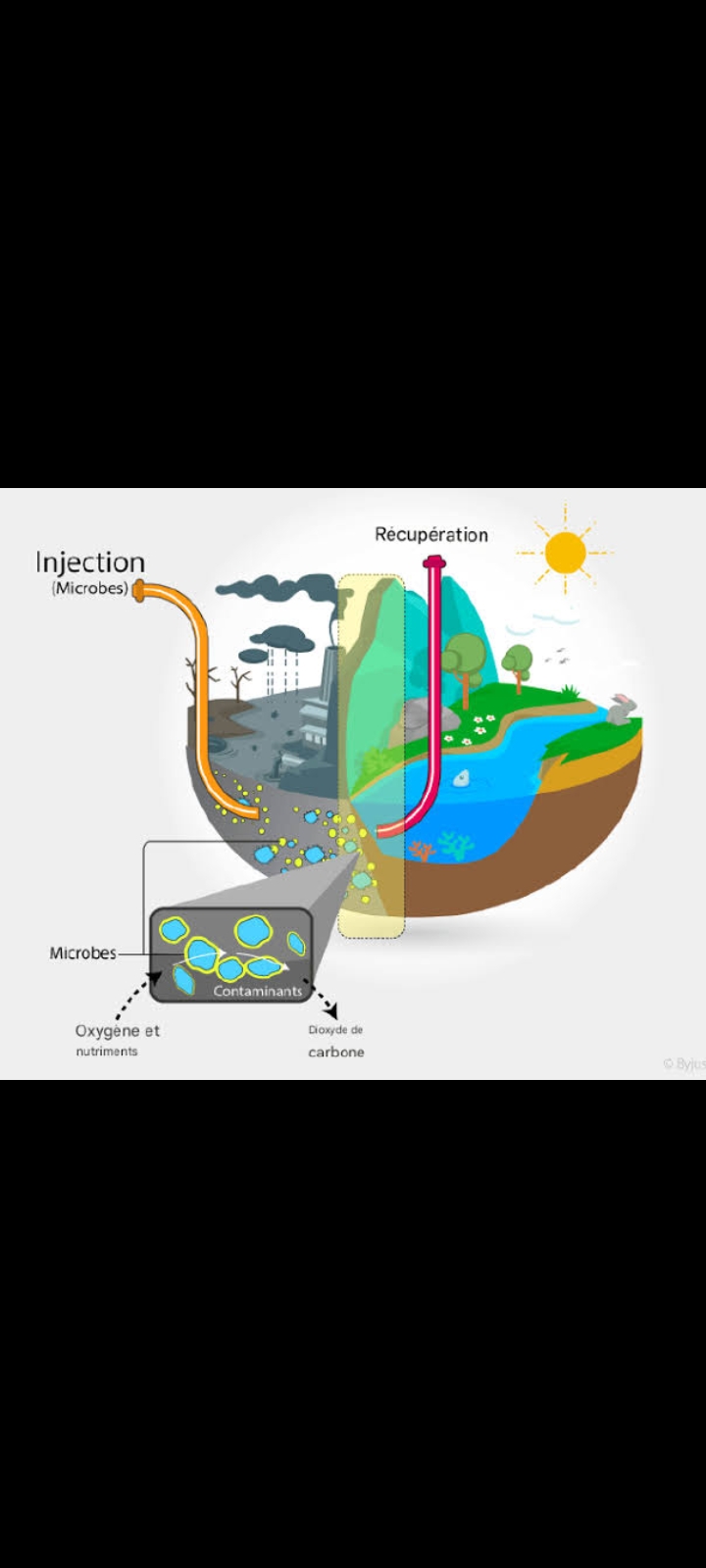
Le traitement des eaux et la dépollution des sols sont des processus complexes nécessitant une approche intégrée et multidisciplinaire. Ces techniques visent non seulement à éliminer les contaminants, mais aussi à restaurer les écosystèmes et à protéger les ressources en eau pour les générations futures.
- Enseignant: bendjebara salima
- Enseignant: Admin User